What is the CO2 footprint of different alcoholic beverages?
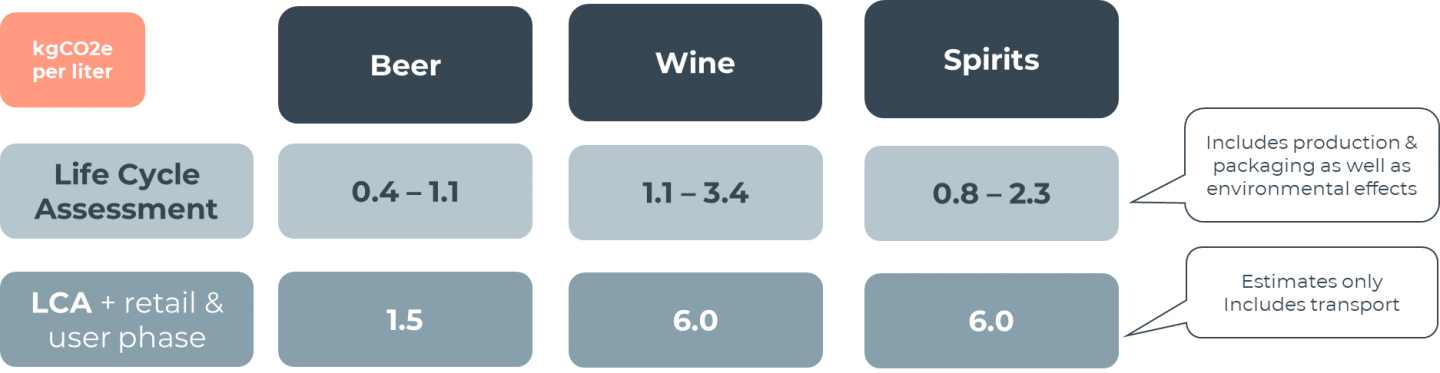
Key factors
- Yield in relation to acreage
- Energy consumption (e.g., for processing, distillation, refrigeration)
- Choice of container (glass bottle, can, plastic)
- Transportation distance
What is the CO2 footprint of different alcoholic beverages?
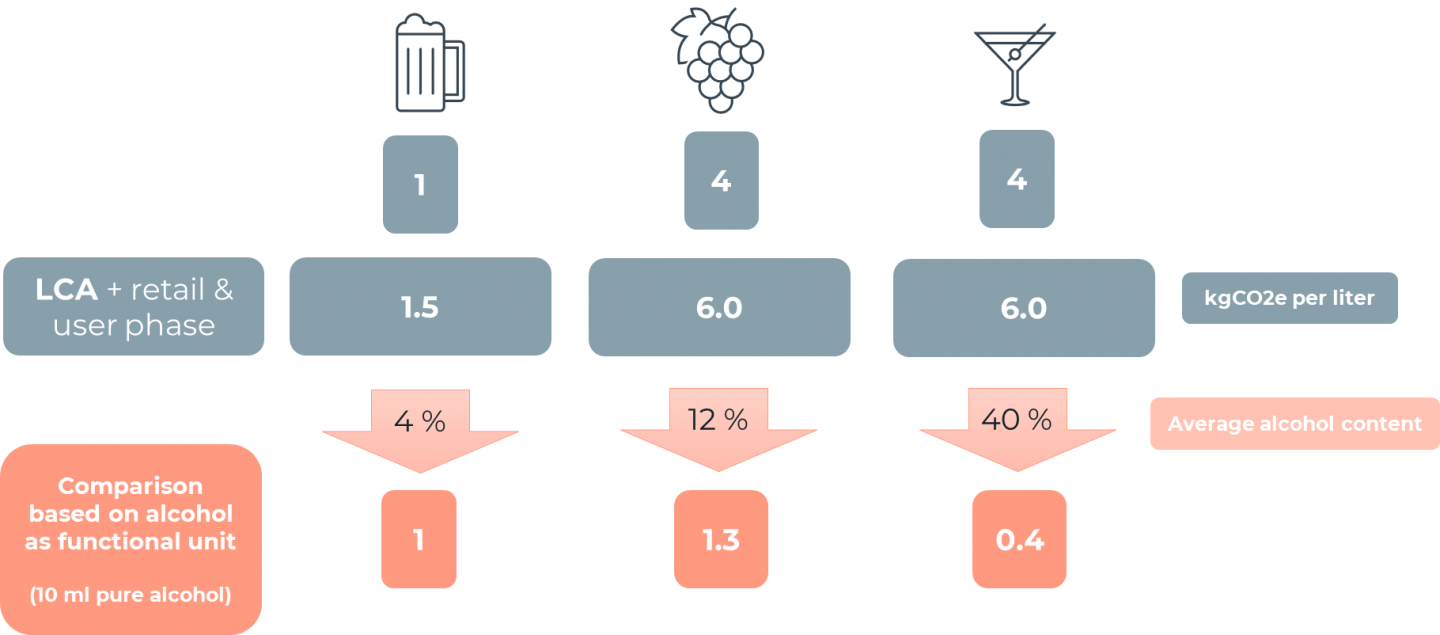
Are natural wine and alcohol-free beer more environmentally friendly?
Natural wine: YES
- No pesticides, no synthetic elements
- Mostly use of biodynamic wine practices
- Wine is not clarified
- But: packaging & transportation remain as strongest contributors to CO2 footprint
- Most significant impact is on the consumer
Alcohol-free beer: YES
- Less water is used during brewing process
- Less waste created
- But: potential adverse effects if artificial components are not handled correctly or require more energy
- Can be seen as substitute of both regular beverages and beer
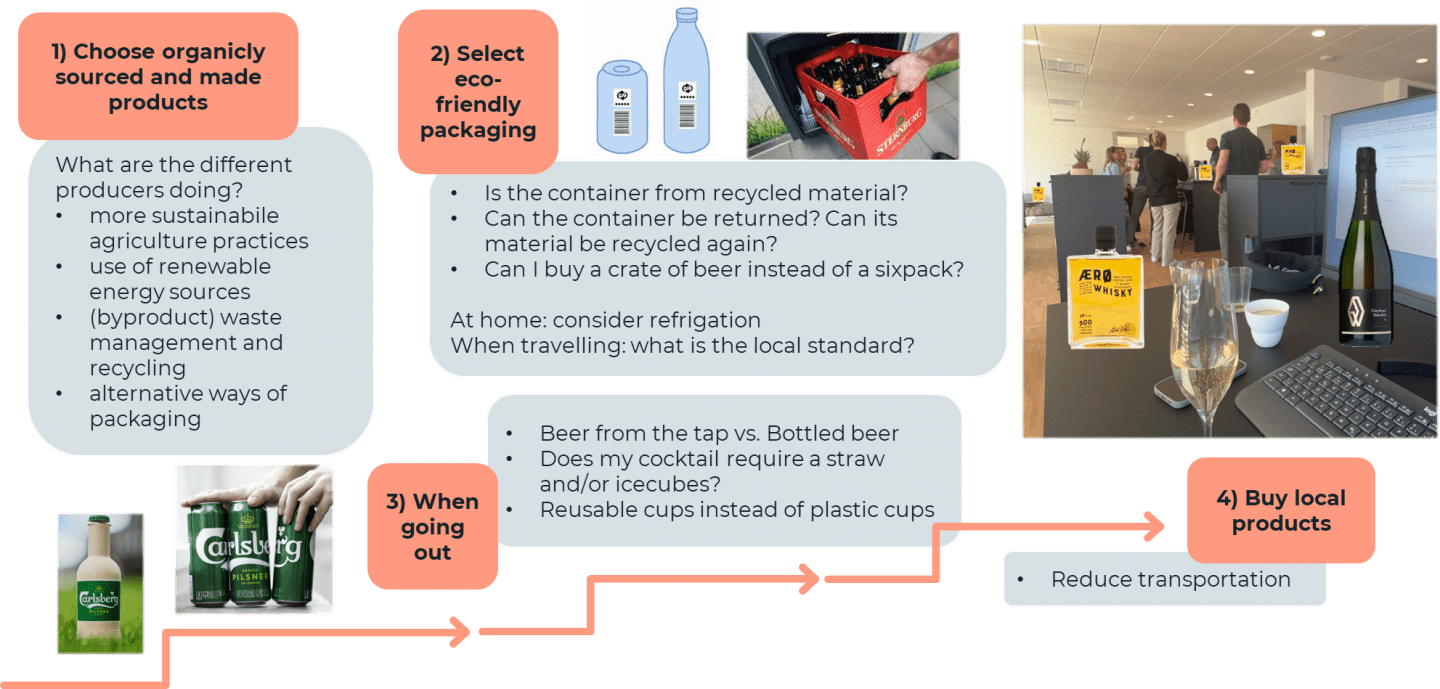
How Can I Drink More Sustainably?

Author: Paula Graetke, Junior Consultant
Sources:
- Saxe, H. (2010). LCA-based comparison of the climate footprint of beer vs. wine & spirits. Fødevareøkonomisk Institut, Københavns Universitet. Report No. 207
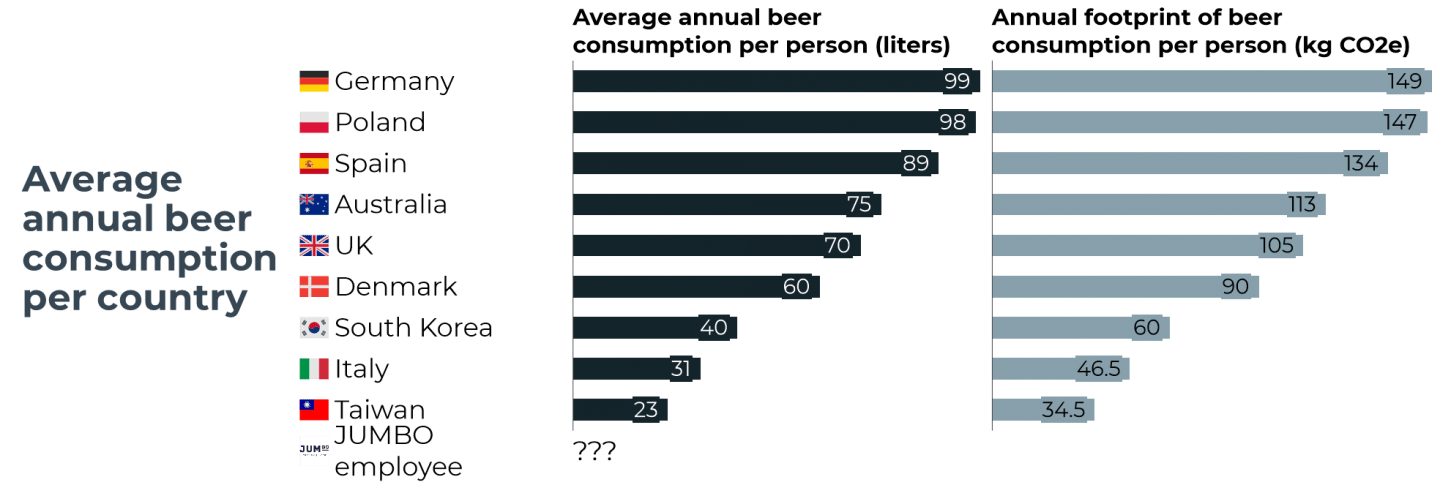
- Beer consumption per country https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_beer_consumption_per_capita
- Is natural wine better for the planet? https://www.themomentum.com/articles/is-natural-wine-better-for-the-planet
- Sustainability & alcohol-free beer https://www.lightdrinks.co.uk/blogs/latest/sustainability-alcohol-free-beer#:~:text=However%2C%20because%20the%20fermentation%20process,the%20production%20of%20regular%20beer
- The Carbon Footprint of Alcohol https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/carbon-footprint-alcohol-getbevvi/#:~:text=And%20ultimately%20leads%20to%20consequences,of%20around%20276%20million%20cars.
- Green Tips: The carbon footprint of alcohol https://www.parkrecord.com/opinion/green-tips-the-carbon-footprint-of-alcohol/
- Data on additional spirits & cocktails: https://8billiontrees.com/carbon-offsets-credits/carbon-ecological-footprint-calculators/carbon-footprint-of-wine/